The Sun is not just a source of light and warmth; it is the heart of our Solar System. Its importance is immense, both for our planet and for understanding the universe. Without the Sun, life as we know it would not be possible. Let’s explore some fun facts, scientific insights, and activities that can help kids and beginners appreciate the Sun’s role in our lives.
The Sun’s Role in the Solar System
The Sun is a massive star located at the center of our Solar System, and it holds more than 99% of the Solar System’s mass. Its gravitational pull keeps all the planets, including Earth, in orbit. Without the Sun’s gravitational influence, Earth and other planets would drift off into space. The Sun is composed primarily of hydrogen and helium and produces energy through nuclear fusion. This energy is what powers everything from the warmth we feel on Earth to the photosynthesis that plants use to grow.

Fun Fact: Did you know the Sun is so large that over 1 million Earths could fit inside it?
The Sun’s Energy and Its Impact on Earth
The Sun’s energy is vital for life on Earth. The light and heat from the Sun make Earth a habitable planet. Without this energy, there would be no warmth, no weather, and no seasons. The energy from the Sun also drives the water cycle, which helps produce rain, rivers, and lakes. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to make their own food. This makes the Sun directly responsible for the food we eat.

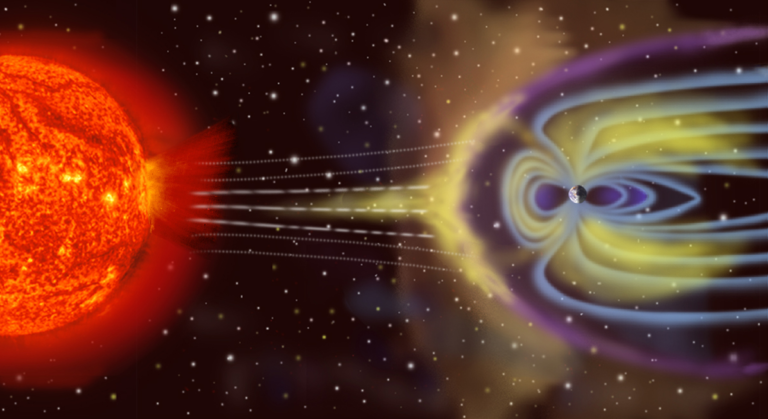
In addition to light and warmth, the Sun also emits solar wind, a stream of charged particles. This solar wind interacts with Earth’s magnetic field, causing phenomena like the auroras, also known as the Northern and Southern Lights. These beautiful displays are a result of solar activity, and they offer an exciting way to introduce children to the dynamic relationship between the Earth and the Sun.
Fun Facts about the Sun
- The Sun’s Surface Temperature: The surface of the Sun, known as the photosphere, is around 5,500°C (9,932°F), while its core reaches temperatures of about 15 million°C (27 million°F).
- The Sun is a Star: Even though it looks big and close to us, the Sun is actually a middle-aged star, and there are billions of other stars in the universe that are much larger and more distant.
- Sunspots: The Sun’s surface has dark spots known as sunspots. These are cooler areas on the Sun’s surface that appear darker. Scientists study these spots to understand solar activity.
Fun Activities for Kids
Introducing kids to the Sun’s amazing features can be both fun and educational. Here are a few simple activities:
- Solar System Model: Build a model of the Solar System using balls of different sizes to represent the planets and the Sun. This hands-on activity will help children understand the Sun’s central role.
- Shadow Tracking: Encourage children to track their shadows throughout the day. By observing how the shadows change, they can learn about the Sun’s movement across the sky and the way it affects our world.
- DIY Solar Oven: Use a pizza box, aluminum foil, and plastic wrap to create a simple solar oven. This activity demonstrates how solar energy can be used to cook food, providing a tangible example of the Sun’s power.
- Aurora Borealis Art: Use bright-colored paints or crayons to create an art piece inspired by the Northern Lights, helping kids visualize solar wind interactions with Earth’s atmosphere.
Current Research and Ongoing Studies
Ongoing research in solar physics continues to reveal new insights about the Sun. NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, launched in 2018, is the first spacecraft to “touch” the Sun, traveling closer to it than ever before. The spacecraft is gathering data on solar winds and the Sun’s magnetic fields, providing vital information on how solar activity affects space weather. Solar research is crucial not only for understanding the Sun but also for predicting space weather events that can impact satellite communications, power grids, and even astronaut safety.
Recent studies have also explored how the Sun’s cycle of solar activity affects Earth’s climate. The Sun goes through an approximately 11-year cycle of solar maximum and minimum. During the solar maximum, sunspots and solar flares are more frequent, which can have an impact on space weather and even Earth’s climate. By studying the Sun’s behavior, scientists hope to predict and prepare for solar storms that could affect modern technology.
Conclusion
The Sun is central to life on Earth, providing energy, warmth, and influencing the climate. By learning about its importance and engaging in fun activities, kids can develop a deeper appreciation for this vital star. Exploring the Sun not only helps us understand the basics of astronomy but also the profound connections between space science and our daily lives. The Sun’s fascinating characteristics and the ongoing research surrounding it ensure that we continue to unlock its many mysteries.